Have you tried to increase your search engine rankings by investing all of your time, money, and effort into methods like keyword research and backlinks? While those on-page and off-page search engine optimization strategies can certainly help, you cannot forget about technical SEO, an often overlooked part of the ranking puzzle that we will cover in this guide.
Be sure to check out our List of Technical SEO Audit Tools and Software when you are finished reading.
What is Technical SEO?
Some consider technical SEO a part of on-page SEO since some of their methods or tactics overlap and intersect. For this guide, we will keep them separate. Although its definition will differ according to source, technical SEO essentially refers to the methods used to create and optimize websites so they can be easily crawled, indexed, and rendered by search engines.
Even with the best content in the business, an eye-catching design, and a bevy of backlinks, a site lacking technical SEO will fail to reach its potential. With the proper technical SEO strategy in place, you can enhance your rankings and visibility on the search engine results pages (SERPS). What makes up a comprehensive technical SEO strategy? Addressing issues like URL structure, page speed, user-friendliness, and more, which we will discuss in further detail.
Read: Internet Marketing vs SEO
Technical SEO vs. On-page SEO
As mentioned, some feel as if technical SEO falls under the on-page SEO umbrella since some of their methods overlap, such as page speed, user-friendliness, mobile-responsiveness, etc. And while that is true, and they are also similar since you can control both technical and on-page SEO since they deal with your site and not external factors, they do differ and should be considered separately, so nothing gets lost in the shuffle when trying to achieve your ranking potential.
True to its name, on-page SEO encompasses things on your website. Through on-page SEO elements like titles, meta descriptions, content, header tags, images, calls to action, and more, you can tell search engines and visitors what your site is about. Simplistically, you could look at on-page SEO as the front end of your site that the visitor sees, while technical SEO is the back end containing the scripts, codes, etc., that deal with your site’s speed, security, and overall infrastructure.
If you are new to SEO and are unfamiliar with some of its tactics, here is a brief on-page SEO checklist to get you up to speed:
- Title – Also called the title tag or page title, this gives context to search engines and visitors what a page is about. You can view the title tag in the SERPs as a clickable link or in the browser window. As such, the title should be informative, relevant, and compelling/actionable to entice clicks and drive traffic. It should also include your primary keyword naturally and be 70 characters maximum to avoid cutoff.
- URL – The URL is the web address users input into a browser to visit a specific page. It is also the link users click on to go to a site. The URL should be in lower-case, descriptive yet concise, have one to two keywords, use HTTPS to build trust, not contain stop words (or, a, an, for, etc.), and avoid any dates to appear as fresh as possible.
- Meta Description – Under each page title in the SERPs sits the meta description, a tag that gives a short summary of what the page is about. The meta description can help users understand what your page offers and increase the click-through rate if appropriately written. To ensure this, keep it at one to two descriptive sentences, under 220 characters (120 for mobile), and be sure to include your keyword, make it compelling, and include a call-to-action to entice the click.
- Header Tags – The H1 to H6 tags can help readers scan a page quickly to get the gist of what it offers and find the exact info they seek. They can also give your page organization and differentiate paragraphs from other text types. Proper headers should contain keywords that differ from your page’s title. The H1 and H2 headers should contain the most essential keywords. Here is a list of SEO Headers: Best Practices and Tips.
- Image Optimization – Images are also another essential element of on-page SEO. Your images should be compressed, original, high-quality, and captivating, have custom file names so Google can detect what is in the picture, and have alt text that offer descriptions if they fail to load.
- Content – A solid on-page SEO strategy stresses high-quality content. Yours should be unique and original, plus up-to-date to reflect current events and info. Content length should be at least 300 words, with more to make it SEO-friendly and valuable to readers. Use keyword-rich phrases in your headlines and content to help readers and search engines decipher what you are writing about.
- Calls To Action – A call to action (CTA) compels a user to click a link or take desired action to increase your conversions, sales, etc. The best calls to action start with a verb, include urgency, use whitespace so they stand out, are big and colorful, and sit at the top or bottom of the page.
Are those the only on-page SEO elements? No, but they are some of the most important ones you can focus on to improve your rankings.
You can more by reading our comprehensive guide: What is On-Page Search Engine Optimization?
We also have a great article discussing the best SEO Tools for On-page SEO.
Technical SEO vs. Off-page SEO
As its name suggests, off-page SEO deals with practices that do not relate to items or content on your site. Instead, off-page SEO focuses on things on outside platforms or websites that you do not have any control over. It uses votes of confidence from links from other sites (aka backlinks) to let search engines know how useful and popular your page is. The higher quality and quantity of backlinks you have and the more brand mentions you get, the higher ranking you can achieve.
Here is a quick summary of some of the top off-page SEO tactics you can combine with technical SEO methods (which we will reveal in a minute) to improve your ranking:
- Link Building – A link-building strategy involves getting other sites (hopefully highly-respected ones) to link to yours. These are called backlinks, and they can be gold for any SEO strategist looking to boost rank. Through link building, you pass authority from high-quality sources to your page. This vote of confidence can lead to a higher ranking since it shows Google that your content is relevant and trustworthy, and that can lead to more visitors to your site. It is worth mentioning that quality is much more important than quantity when it comes to backlinks.If you have thousands of backlinks from spammy sites, you probably will not see any improvement in your ranking.To build links, you should start by loading your site with unique, high-quality content worthy of such attention. You can also build links manually through blog comments, guest posts, press releases, etc. Requesting backlinks is another link-building method, which involves contacting website owners seen as industry leaders in your niche.Here is a great companion piece to learn more about Link Building Strategies for SEO.
- Content Marketing – This off-page SEO tactic deals with creating shareable infographics, whitepapers, eBooks, studies, research papers, surveys, etc., to attract links. Here are some great Tips for Content Marketing.
- Guest Posting – One of the best ways to build links is through guest posting. With it, you create captivating content, submit it to another site, and get yourself in front of a new audience. This can generate traffic to your site and grow your reputation as an authority in your niche.
- Influencer Marketing – You can collaborate with influencers on social media platforms like Instagram, YouTube, TikTok, etc., to leverage their traffic and attract new viewers to your site.
- Local SEO – Some like to keep local SEO separate from everything else, but it could be considered part of off-page SEO. Local SEO uses Google My Business, citations (listings containing your company address, phone number, etc.) to increase rankings specific to certain locations. Here are some Local SEO Tips you can try to promote your website.
- Reviews – While overlooked, reviews are essential to off-page SEO since they can increase conversions via trust. Beyond that, online reviews can also help Google understand your site and provide positive brand signals to boost your ranking.
- Social Media Optimization – Although social shares are not a direct ranking factor, you can look at social media as another search engine to expand your reach. Since many people use social media as a primary point of contact with a brand, be sure to use platforms to share content, provide customer service, and engage to drive traffic and increase your conversions. We have gathered up a list of some of the Best Social Media Optimization Tips for Internet marketers and web developers.
What are the Benefits of Technical SEO?
Many people overlook technical SEO because it seems complicated and out of their range of knowledge. Why should you invest time and effort into technical SEO? Besides the obvious answer of increasing visibility and generating more traffic so you can boost your business or brand, it is because a properly implemented technical SEO strategy can provide the following benefits:
- You can pinpoint SEO problems – A technical audit can help you spot issues with broken links, duplicate content, a messy site architecture, and more that are hampering your ranking potential.
- Improved ranking – If your site’s technical SEO is up to snuff, you could land on the first page of the SERPs, which is where most clicks occur.
- A more crawlable, indexable, and rankable site – Search engines have bots that scour your site to collect critical information. If your site is not crawlable, the bots will not be able to access and index all of your content, which can negatively impact your ranking.
- Enhanced security – There are technical SEO tactics that can enhance your site’s security to improve the user experience and help Google give you a ranking boost for your efforts.
- A better user experience – The Internet is a highly competitive place. If your site fails to deliver in terms of speed, has broken links, is hard to navigate, or has other issues like irritating popups, visitors will quickly move on. If your bounce rate is high, search engines will see your site as unworthy of a high ranking.
- Keeping up with mobile times – Most people access the Internet on the go via their mobile devices. If your site is not mobile-friendly, you will take a reputation hit from users and a ranking hit from search engines.
- Google compliance – Stick to Google’s best practices for SEO using all of the technical tactics we are about to list, and you can get rewarded with higher rankings from the search engine.
Technical SEO Checklist
What makes up a comprehensive technical SEO strategy? All of the elements in the checklist below.
URLs
A basic yet essential part of any technical SEO strategy is your URL structure. If done correctly, your URL’s appearance tells searchers and search engines what your page is about.
For example, if your URL starts with HTTPS, that says your page uses Hypertext Transfer Protocol and the Secure Socket Layer (SSL). In simple terms, that “S” at the end says that you are using the security protocol that keeps the page’s content and your visitors’ information secure:
https://www.htmlgoodies.com/cms/best-wordpress-drag-and-drop-page-builders/
Beyond the beginning of the URL, you can see that it also reflects what is on the page, which is the site (HTMLGoodies), the section or category (CMS), and the title of the post (Best WordPress Drag and Drop Page Builders). To get the best ranking, make sure your page URLs follow a similar, sensible structure that does not keep the searchers or search engines guessing.
Breadcrumbs
Breadcrumbs are a type of navigation that form a visual trail visitors can use to backtrack to where they started. A breadcrumb menu does this by telling a visitor how the page they are currently on relates to the rest of the website.
For instance, if you are on a clothing website, a breadcrumb menu at the top could look like this:
Home > Shoes > Athletic Shoes > Basketball Shoes
By seeing those breadcrumbs, you can click on Athletic Shoes to go back a page and look for running shoes, or click on Shoes to go back two pages and search for sandals, dress shoes, etc.
For user-friendliness, breadcrumbs should be highly visible to visitors so they can navigate your site without having to use the clunky Back button. But since search bots also use breadcrumbs, they should have a structured markup language that provides accurate context when your site is crawled.
SSL
SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer. It makes your site more secure by providing a protective barrier between the web server, which fulfills an online request, and the browser. When can SSL’s added security really come into play? When a visitor enters personal contact or payment info into your site. With SSL protection, hackers will have a much harder time stealing such data.
You probably are more familiar with SSL than you think. If you have ever looked at the URL bar of a browser and seen https:// and a lock symbol at the beginning of a web domain versus the standard https://, that means that the site had an SSL certificate. How can it affect your page’s user experience? Positively since many suggest that web users avoid entering info into sites that lack https or the lock symbol. If you ask for sensitive data without those added comfort symbols, you may not get it, as visitors may feel as if they are at risk for hacking.
Visitors are not the only ones who value SSL, as so do search engines. In 2014, Google announced that SSL would be a ranking factor. As such, you should make it a priority to set your preferred domain to your home page’s SSL variant.
You will need to migrate non-SSL pages on your site from http to https once SSL is set up. While time-consuming, it is an essential move to making your site secure, giving your visitors peace of mind, and adhering to Google’s wishes for SEO.
You can migrate non-SSL pages by doing the following:
- Redirect all http pages on your site to their https counterparts.
- Update all of your Hreflang and canonical tags.
- Update the URLs on your robots.txt and sitemap.
- Create a new version of Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools for your https site. Make sure all of the traffic migrates over by tracking them closely.
Technical Audits
A technical SEO audit will let you know if there are any gaps or errors in your technical SEO strategy. It can check your website’s health and let you know of any issues that must be fixed to get the highest search engine ranking possible and avoid losing traffic to your competitors.
How often should you conduct a technical audit? That answer varies depending on who you ask, but some suggest doing a mini audit each month, and performing a full technical SEO audit every four to five months. A proper audit can take about an hour for those who are experienced. Beginners can complete technical audits within a few hours, provided they know what steps to take or use the proper SEO tools.
Several SEO tools can simplify the auditing process. Not only can they help with technical SEO, but they may also have features that check your site’s on-page and off-page SEO for any glaring issues. Here are some of the top technical audit tools that can also help you via other SEO-friendly features:
- Semrush – Offers free audits for 100 web pages. Scans sites for 130-plus technical and SEO issues. Read our SEMRush Review for more on this popular SEO tool.
- GTMetrix – Checks technical health in terms of page loading speed, caching, scripts, etc.
- OnCrawl – A technical SEO platform that checks your site for search indexation, sitemaps, pagination, Hreflang tags, site architecture, page loading speeds, content quality, and more.
- SE Ranking – Pinpoints user experience problems and crawls your site link-by-link while offering actionable solutions.
- DeepCrawl – Reviews canonical tags, tests XML sitemaps, offers special audits for eCommerce pages, etc.
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider – An installable tool that performs technical SEO audits to look for broken links, server errors, and other issues.
- Google Search Console – Formerly Google Webmaster Tools, Search Console offers technical audits to find accessibility and indexation issues while providing data on broken links, content quality, Accelerated Mobile pages, and more.
- Ahrefs – Use it to find problems with redirects, broken pages, duplicate and thin content, page performance, CSS and JavaScript resources, etc. Here is our Ahrefs SEO Software Review.
Example of SEMRush Interface
Some of those tools will cost you for their services. And while they may be convenient, they are not the only auditing option, as you can also perform manual audits on your own. Here are some steps involved if you decide to conduct a manual SEO audit for technical issues:
- Crawl your site to look for problems.
- Review your sitemap and optimize it.
- Check to see that your website has just one browsable version.
- Review your internal links.
- Audit your backlinks.
- Look over your HTTPS content.
- De-index any pages of low value.
- Check your site speed and make the necessary moves to improve it.
- Compare site metrics with Google Analytics.
- Re-crawl your site.
Here is our pick for the Best SEO Software (Paid and Free Tools).
HTML, JavaScript, CSS
HTML, JavaScript, and CSS are programming languages often used in technical SEO discussions. If you are unfamiliar with them, here is how they come together as one to create an optimal site that is user-friendly and worthy of a high ranking:
- HTML – Represents your site’s foundational code that gives browsers what they need to display your content. Headers and listicles on a site are examples of HTML.
- JavaScript – The code that adds interactive, flashy, and dynamic elements to your pages, such as a click-through quiz.
- CSS – The programming that adds visual appeal and deals with your site’s appearance, such as the overall design, fonts, and colors.
Read about the best HTML, CSS, and JavaScript Tools and Libraries.
Crawling and Crawlability
Ensuring site crawlability is essential to any technical SEO strategy. Search bots must crawl your web pages so they can collect information about your site. If they cannot do their job, they will not be able to index or rank your pages.
How can you make your site more crawlable? Here are some tips:
- Create and submit your XML sitemap – An XML sitemap is a critical file that details all of your site’s top pages. It acts like a map that helps search bots understand your site’s structure so they can crawl your pages. Once your sitemap is complete, you need to submit it to Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster tools. If you add or delete any web pages, you will need to update your sitemap.
- Make the most of your crawl budget – Your crawl budget represents what search bots will crawl on your site, whether pages or resources. Since it is not infinite, you will have to prioritize your top pages for crawling to get the most SEO bang for your buck. Ways to maximize your crawl budget include keeping your sitemap updated, getting rid of outdated or unnecessary content, fixing or redirecting broken links, canonicalizing or deleting duplicate pages, and ensuring your JavaScript and CSS files are crawlable.
- Follow a set URL structure – You want your URLs to follow a set structure, so they make sense and do not differ logically from page to page.
- Maintain an organized site architecture – As with your URLs, your site structure or information architecture should be designed in a way that is organized and makes sense. Any related pages should be grouped together so that search bots can easily understand how they are related to one another. For example, if you have a blog, the homepage should link to blog posts, and each post can link to author pages.
Use robots.txt
Web robots will crawl your site by first looking for the Robot Exclusion Protocol, or /robot.txt. This lets or prevents specific robots to crawl your site or specific sections or pages. Since malicious bots that spam your forums or scrape your content exist, you may want to block them from crawling your site. Robot.txt will allow you to do just that. You can also use it to keep search bots from wasting your crawl budget on unnecessary data by excluding pages like a login or Thank You page.
Indexing
You can think of indexing as Google’s file cabinet. After a search bot crawls a site, stores the content, and finishes indexing, the page will appear in the SERPs if it matches a user’s query. You can make sure Google properly crawls and indexes your content by using the Google Search Console. This free tool lets you submit sitemaps to help Google catalog your content and see when a new page has been indexed.
Use HTML for your main navigation features to avoid any indexing issues, as Google may have trouble indexing complex navigational structures in JavaScript. Make sure your navigation is complete as well, so the Googlebot can easily jump between links. Also, check that your site’s desktop and mobile versions are the same. Content variations can prevent proper indexing.
Rendering
Rendering is a process where a web browser builds a web page that was requested so visitors can see a user-friendly version of the website minus all of the complicated code. It occurs as follows:
- The Googlebot retrieves your web pages.
- It runs your code.
- It assesses your content so it can figure out your site’s layout and structure.
The more efficient the rendering process, the higher the Core Web Vitals scores. The less efficient the rendering, the more issues you may have with page crawling, advertising income, and sales.
Sites used to be a lot easier to render when they used HTML and lacked JavaScript. Now that JavaScript plus CSS are highly-used, rendering has become more of a chore for Google.
While JavaScript, CSS, and other complex code can make your website pop, remember that they can hinder the rendering process and make it less accessible. To improve accessibility, Google recommends using content that is pre-rendered.
Structured Data
You want to make it as easy as possible for Google to understand your website’s content. One of the best ways to do so is by building structured data, which creates a highly-detailed site description in a Google-friendly code or schema.
A great way to become more familiar with this technical SEO tactic is to use Google’s very own Structured Data Markup Helper or Codelabs.
Page Speed
Search engines could easily render website pages in the “old days” of the Internet, as site elements and programming were rather basic. Nowadays, web content is much more advanced and dynamic since developers can leverage the power of CSS and JavaScript, making page speed a critical ranking factor and part of the user experience.
Statistics show that users are not too patient when it comes to page speed. The more time your page takes to load, the more they start to contemplate going elsewhere. According to Think with Google research, bounce rate significantly increases quite quickly, all within a 10-second span, and here is proof. As page load time shifts from:
- One to three seconds, bounce rate probability increases 32 percent.
- One to five seconds, bounce rate probability increases 90 percent.
- One to six seconds, bounce rate probability increases 106 percent.
- One to ten seconds, bounce rate probability increases 123 percent.
As you can see, it does not take much to turn a user off, which is why improving your page speed should be one of your top priorities when devising a technical SEO strategy. Here are some ways to make your page speed faster:
- Make your code more concise – Your site speed can be slowed down by bloated and inefficient code. Do your best to clean up and trim your code so your page can load quicker. Once it is trimmed, you can minify and compress it, so it is not responsible for negatively impacting your user experience.
- Use a custom theme – While they can cost more, custom-made themes may lead to better page speed, unlike their pre-made template counterparts, which often come with unnecessary code.
- Be picky with plugins – It can be tempting to install every plugin available to give your site the most bells and whistles possible. However, too many plugins can slow down your site. Beyond minimizing plugin use beyond the essentials, you should also ensure that they are all up to date to avoid security issues that can hurt your rankings.
- Install a cache plugin – Speaking of essential plugins, one example would be a cache plugin that keeps a static version of your site on file that it sends to returning visitors. In doing so, users can enjoy shorter load times on subsequent visits.
- Audit your redirects on a frequent basis – A simple 301 redirect can take a few seconds to complete. Combine those few seconds over multiple pages or redirect layers, and you could significantly slow your site down.
- Use a CDN – A content distribution network is a web server that stores website copies across multiple locations around the world, allowing it to deliver your site according to where the searcher is located. This leads to a shorter traveling distance between servers, which helps your site load quicker.
- Compress everything – Compression can minimize the size of your JavaScript, CSS, and HTML files, plus images to make them more lightweight. This can lead to faster loading times.
Core Web Vitals
In 2021, Google tweaked its ranking algorithm to include page experience. This meant that the search engine giant would place a premium on user experience and site speed, with Core Web Vitals representing a large piece of the puzzle.
What are Core Web Vitals? They are a subset of factors Google uses to calculate a page’s user experience, such as a lack of malware and popups, mobile-friendliness, and HTTPS. Specifically, there are three Core Web Vitals, which are:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) – The time it takes for a page to load from a user’s perspective.
- First Input Delay (FID) – The time it takes for a user to interact with a page.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) – Page stability while loading.
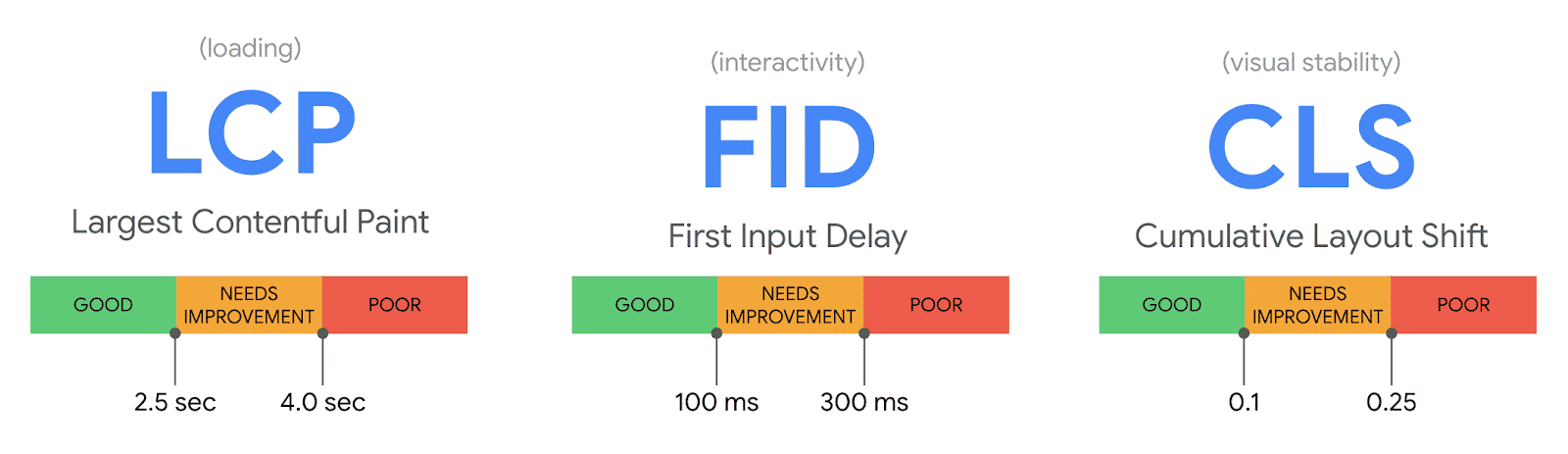
You can view these Core Web Vitals via the enhancements section of the Google Search Console. Here are tips to improve each so you can improve your user experience and boost your rankings:
- LCP – The LCP measures how long it takes for a user to see most of your page’s content after clicking a link. A faster LCP means the user can begin interacting with your page and complete what they intended without waiting. You can boost your LCP by minifying your CSS, getting rid of nonessential third-party scripts and large page elements, upgrading your web hosting, and implementing lazy loading for images.
- FID – The faster your FID, the quicker a user can interact with your page to choose a menu option, click a link, enter their email, etc. FID is particularly important on signup or login pages where users must interact. To improve your FID, you can use a browser cache, eliminate nonessential third-party scripts, and minimize or defer JavaScript on the page.
- CLS – If your page is unstable while loading, the user may have trouble interacting with it. For example, a page that bounces all over the place while loading could force the user to click incorrectly, leading them to an unintended page. And this could lead them to get frustrated and bounce to a competing site. To improve your CLS, place new UI elements below the fold, give your media set size attribute dimensions, and reserve spots for ad elements, so they do not interfere with other content and shift it around.
Read more Core Web Vitals Tips.
User-friendliness
A user-friendly site puts the users’ needs before anything else, including Google. This does not mean that you neglect search engines via your technical SEO methods. It just means that you design your site with the visitor in mind to ensure an enjoyable experience. By doing so, you can keep visitors coming back for more and get the bonus of a ranking boost from Google, as user-friendliness is vital to the search engine.
One way to ensure user-friendliness is through AMP or Accelerated Mobile Pages, an open-source HTML framework Google developed to help web designers create content that prioritizes mobile usage. With over half of web traffic coming from mobile devices like phones and tablets, using AMP can make sure that your users have a smooth browsing experience on the go. Using the AMP framework to build your web content can give users what they want, plus give you preferential ranking from Google since the search engine giant recognizes mobile’s growing popularity.
Another way to make your site as user-friendly as possible is through mobile-first indexing, where developers and search engines prioritize a site’s mobile version for indexing. To see if your site is using mobile-first indexing, head over to Google Search Console and look at your latest crawl log for a page that was recently added to your site. If the Googlebot smartphone crawled that page first, you are now on mobile-first indexing and on your way to a more user-friendly site.
Duplicate Content
While many feel that anything related to content is on-page SEO, remember that on-page and technical SEO sometimes overlap. What is the primary problem with having duplicate content on your site? Google aims to index pages with distinct, unique content. If you have multiple pages on your site that are similar, the search engine will struggle to rank them.
Duplicate content can come in many forms. It could be a blog post or article copied identically elsewhere on your site, but a near-match could also get you in trouble. For instance, if you have an e-commerce site selling shoes with multiple product pages and want to save time, avoid the temptation to use the same shoe description for different brands. Simply changing a title or a line or two on a page may not prevent it from being seen as a duplicate, and this could cause you to take a ranking hit.
Sometimes duplicate content may not be your fault. If you find that a competitor is copying your content and not giving you credit for it, contact them. Ask that they either remove your content or accredit it, so you get the desired ranking results. Another way to avoid the duplicate content issue is to implement canonical tags to mark the original info source, which we will discuss in a moment.
Thin Content
Duplication is not the only content issue you could run into when trying to shore up your technical SEO, as thin content can also be a problem. What is thin content? It could be an article, blog post, or page that is lacking and does not give search engine crawlers enough info to work with.
For example, you may have a website that represents a local cleaning service. However, you do not describe the service being offered on one of the pages, as you only have a list of phone numbers or employees that customers can call. Or, you may lack internal linking on the page, preventing crawlers from heading to other parts of your site. Another example of thin content is having content on a page that does not match the search intent of a user. In short, you want to ensure that each page is complete with relevant, high-quality content and some form of internal linking to make the crawler’s job as straightforward as possible.
Canonical Tags
As mentioned, canonical tags are a way to avoid being penalized for duplicate content on your site. These markers (rel=”canonical”) tell search engines that the URL is a copy or duplicate of a page. Canonical tags are found in a page’s HTML code in the <head></head> section.
When using these tags, do not point (or canonicalize) to a page that redirects to another page (aka 301 redirect). Also, be sure that you only canonicalize to relevant content.
Hreflang
Your on-page, off-page, and technical SEO efforts resulted in a site with a solid Google ranking. Now, you want to expand your reach by letting people in other countries who speak other languages absorb your content as well. How can you do this to achieve your more global goals? By using the Hreflang attribute.
This HTML tag helps search engines decipher the exact language you use on a page. With it, you can show how two pages different in written languages are related. When is the Hreflang attribute essential? When you are looking to target audiences according to their location.
For example, if you own a business in Spain and are opening a new branch in neighboring France, you want to ensure that your French visitors receive the correct page version so they can understand what they are reading. With the “hreflang=fr” tag, Google will know that anyone with a France IP address should get the French page version. By adding this simple tag, you can make your page more accessible and user-friendly, resulting in better traffic and eventual ranking.
HTTP Errors and Error Types
HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) errors can block your site’s critical content from search bots, making their jobs impossible. They can also keep users from accessing your content and make a bad first impression that keeps them from revisiting your site. As such, you will need to spot and fix any HTTP errors as quickly as possible to avoid sabotaging your search engine rankings.
You may encounter several HTTP error types, and each has its own fix. Here are some of the most common ones:
- 301 Permanent Redirect – These redirects can be set up to permanently reroute web traffic from one URL to another. Each 301 redirect can increase your page load time. Have tons of them, and your site could get bogged down, resulting in a frustrating user experience. Make it your goal to have zero redirect chains to keep users happy and to prevent search engines from giving up on crawling your pages.
- 302 Temporary Redirect – You can temporarily reroute traffic from one URL to another with this technique. Users will go to the new page, while the cached title tag, description, and URL will keep in line with the original URL. However, if the temporary redirect remains in place for a certain period, it will get treated as a permanent redirect, passing the cached title, description, and URL to the destination URL.
- 403 Forbidden Message – This HTTP error appears when a user requests content that is restricted due to a server misconfiguration or access permissions.
- 404 Error Page – Tells a user that they requested a page that does not exist either because they typed the incorrect URL or it has been removed. To minimize damage, you can tweak your 404 pages to be engaging and keep your visitors from bouncing off your site.
- 405 Method Not Allowed – An HTTP error that occurs when your web server recognizes yet blocks an access method.
- 500 Internal Server Error – This will appear when your server has problems delivering your site to a requesting party.
- 502 Bad Gateway – An HTTP error that happens when there is an invalid response or miscommunication between web servers.
- 503 Service Unavailable – Your server cannot fulfill a request, even though it is working correctly.
- 504 Gateway Timeout – It took too long for a server to get a response from your web server regarding the information it requested.
Featured Snippets
Have you ever seen the boxes above search results that offer answers to specific questions? Those are called Featured Snippets, and they exist so searchers can quickly get the answers they seek without having to click an extra link. To get placement in these valuable snippets, Google says you will need to provide the best answer to a searcher’s question.
While Featured Snippets may stray from the schema markup, keep them in mind when creating your content, as earning placement above the search results is a great way to get an SEO boost.
Google Discover
Over half of searches come from mobile devices, and that number is likely to climb in the years to come. To address growing mobile usage, Google came up with Google Discover, a tool that lets users customize a content library by picking their favorite categories, such as politics, music, sports, etc., so they can see stories and updates aligned with their interests. If you do not personalize it, Google Discover displays data according to your search history by default.
Since Google Discover is still somewhat new and a bit difficult to figure out on the SEO side, some believe that you can increase your chances of placement on the feature by following the topic cluster model. Succeed, and you could enjoy the traffic and SEO boost that comes with a user base that is highly engaged and receives a steady stream of your content.
Read more Search Engine Optimization (SEO) tips, tutorials, and SEO Tool reviews.